The Federal Reserve's interest rate, commonly referred to as the fed rate, plays a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of not just the United States but the entire world. It serves as a critical tool for controlling inflation, managing economic growth, and stabilizing financial markets. As the central bank of the United States, the Federal Reserve's decisions regarding the fed rate have far-reaching implications that can affect everything from mortgage rates to international trade balances.
Understanding the fed rate is essential for anyone looking to make informed financial decisions. Whether you're a business owner, investor, or simply someone managing personal finances, staying up-to-date with the Fed's monetary policies can help you anticipate economic shifts and plan accordingly.
This article will delve deep into the concept of the fed rate, its mechanisms, and its impact on various sectors. By the end, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of how the fed rate influences your financial well-being and the broader economy.
Read also:Grand Ole Opry 100th Anniversary Celebrating A Century Of Country Music Excellence
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Fed Rate
- A Brief History of the Fed Rate
- How the Fed Rate Works
- Factors Influencing the Fed Rate
- The Impact of Fed Rate on the Economy
- Fed Rate and Its Influence on Investors
- How Fed Rate Affects Consumers
- Global Implications of Fed Rate Changes
- Predicting Future Fed Rate Movements
- Conclusion
Introduction to Fed Rate
What is the Fed Rate?
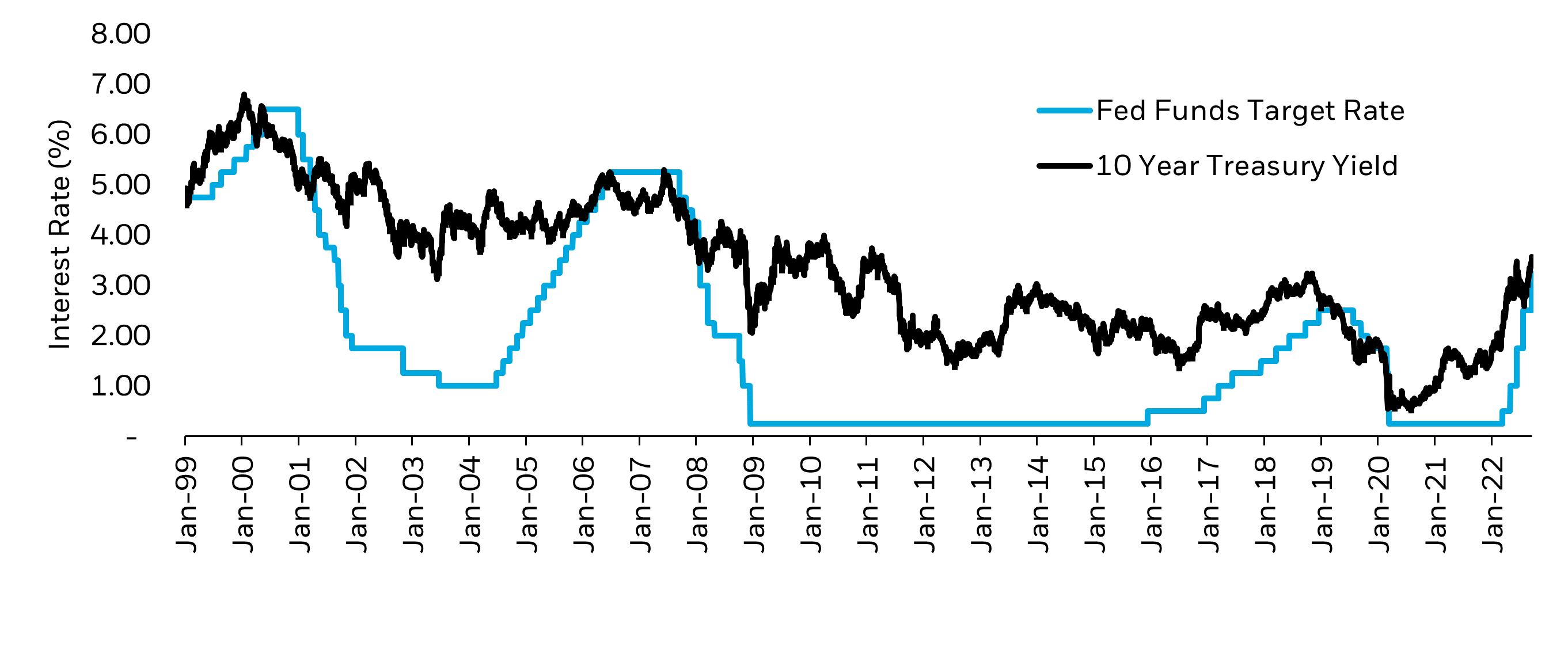
The fed rate, officially known as the federal funds rate, is the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to other banks on an overnight basis. This rate is set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which is the monetary policymaking body of the Federal Reserve System. The fed rate serves as a benchmark for other interest rates, influencing everything from credit card rates to mortgage loans.
Why is the Fed Rate Important?
The importance of the fed rate cannot be overstated. It acts as a lever to control inflation and maintain economic stability. By adjusting the fed rate, the Federal Reserve can either stimulate economic growth during downturns or cool down an overheating economy. This delicate balancing act is crucial for maintaining a healthy economy.
A Brief History of the Fed Rate
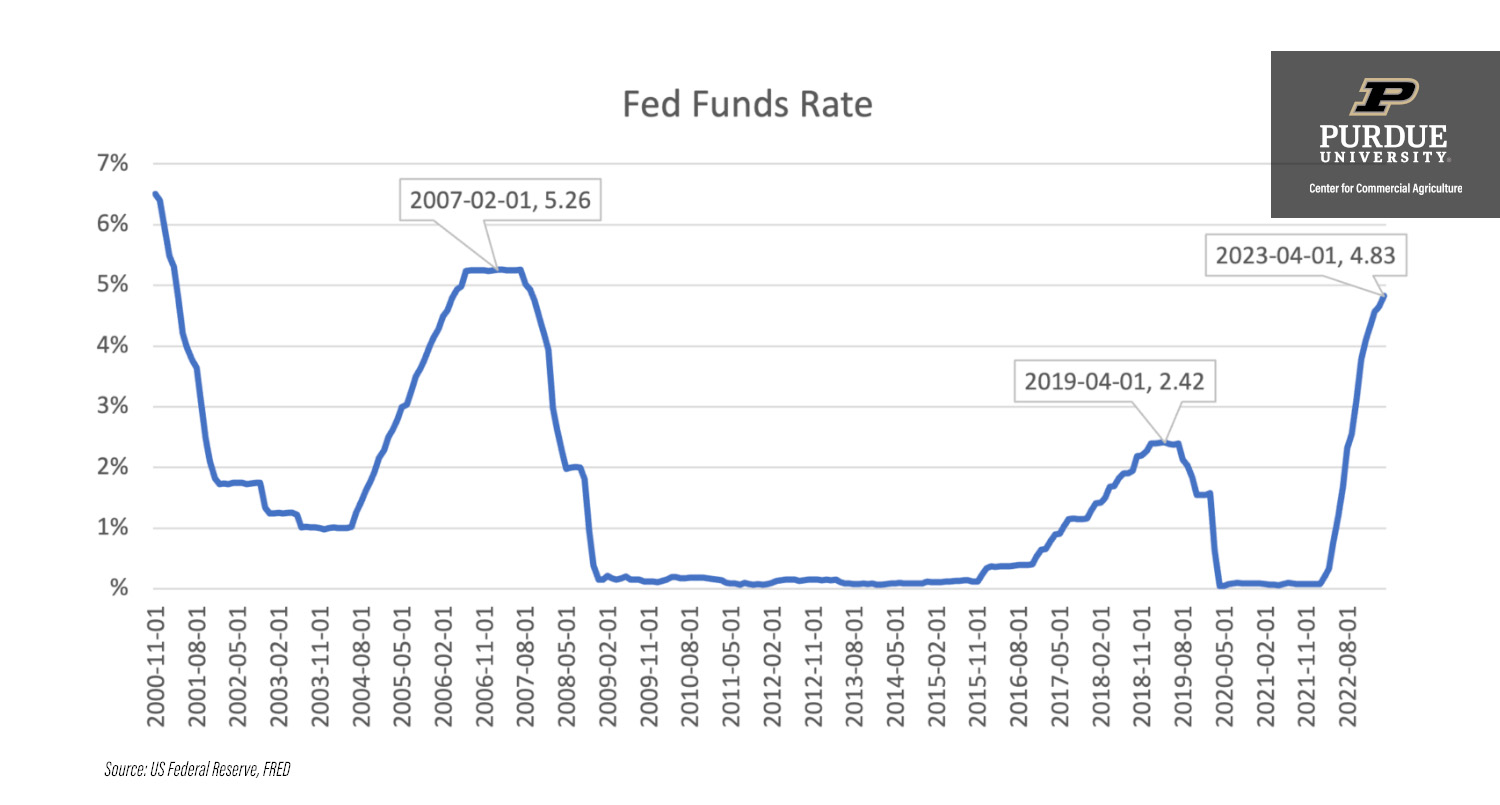
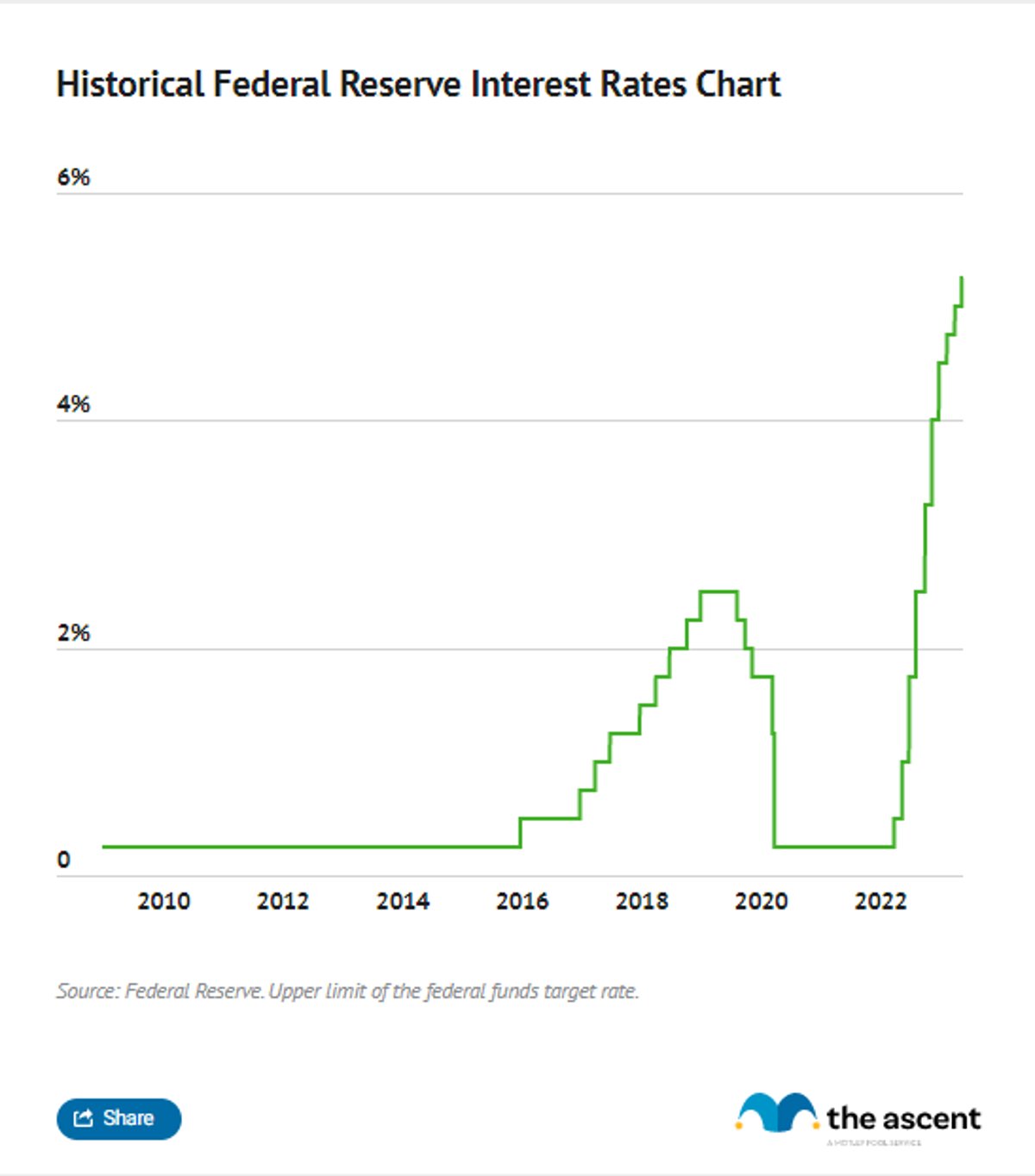
Since its inception in 1913, the Federal Reserve has used the fed rate as a tool to manage economic conditions. Over the decades, the fed rate has fluctuated significantly, reflecting the economic realities of each period. For instance, during the 1980s, the fed rate soared to combat high inflation, while in the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, it was drastically reduced to near-zero levels to stimulate recovery.
How the Fed Rate Works
Setting the Fed Rate
The process of setting the fed rate involves regular meetings of the FOMC, where members analyze economic data and forecasts to determine the appropriate level for the rate. The committee considers factors such as inflation, unemployment, and economic growth when making their decisions.
Implementation of the Fed Rate
Once the fed rate is set, it is implemented through open market operations, where the Federal Reserve buys or sells government securities to influence the money supply. This mechanism ensures that the actual overnight lending rate aligns with the target fed rate.
Factors Influencing the Fed Rate
- Inflation: High inflation often prompts the Fed to raise the fed rate to reduce spending and borrowing.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth may lead to higher fed rates to prevent overheating.
- Unemployment: High unemployment can result in lower fed rates to encourage job creation.
- Global Economic Conditions: The Fed also considers international economic factors when setting the fed rate.
The Impact of Fed Rate on the Economy
Effects on Businesses
Changes in the fed rate can significantly impact businesses. Higher rates increase borrowing costs, potentially reducing investment and expansion plans. Conversely, lower rates can stimulate business activity by making credit more accessible.
Read also:Julia Bachetti The Rise Of A Remarkable Figure In The Entertainment Industry
Effects on Employment
The fed rate also influences employment levels. By adjusting the rate, the Fed aims to achieve maximum employment without triggering inflation. This balance is crucial for maintaining a stable labor market.
Fed Rate and Its Influence on Investors
Stock Market Reactions
Investors closely monitor fed rate decisions as they can have immediate effects on the stock market. Generally, lower rates are seen as positive for stocks, as they encourage borrowing and investment. However, prolonged low rates can lead to concerns about economic stagnation.
Bond Market Dynamics
The bond market is particularly sensitive to changes in the fed rate. Rising rates typically lead to falling bond prices, as existing bonds with lower yields become less attractive compared to newly issued bonds with higher yields.
How Fed Rate Affects Consumers Impact on Borrowing
Consumers experience the effects of the fed rate through changes in borrowing costs. Adjustable-rate mortgages, car loans, and credit card interest rates are all influenced by the fed rate. Understanding these dynamics can help consumers make better financial decisions.
Savings and Investments
Higher fed rates can be beneficial for savers, as they often lead to higher returns on savings accounts and certificates of deposit. However, for those with debt, higher rates can increase the cost of servicing that debt.
Global Implications of Fed Rate Changes
The fed rate has global implications due to the dominance of the U.S. dollar in international trade and finance. Changes in the rate can affect currency exchange rates, capital flows, and economic policies of other countries. For example, a higher fed rate can attract foreign capital to the U.S., strengthening the dollar but potentially harming export competitiveness.
Predicting Future Fed Rate Movements
Current Economic Indicators
To predict future fed rate movements, analysts examine a range of economic indicators. These include employment data, inflation reports, and GDP growth figures. By understanding these indicators, one can gain insights into the Fed's likely actions.
Long-Term Trends
Looking ahead, the Fed's approach to the fed rate will likely be shaped by long-term trends such as technological advancements, demographic shifts, and global economic integration. These factors will continue to influence monetary policy decisions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the fed rate is a critical component of the Federal Reserve's monetary policy toolkit. It impacts a wide array of economic activities, from business investments to consumer borrowing. By understanding the mechanisms and implications of the fed rate, individuals and organizations can better navigate the complexities of the modern economy.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. Additionally, explore other articles on our site to deepen your understanding of financial topics. Stay informed and empowered in your financial journey!
Data Source: Federal Reserve, Bureau of Labor Statistics, and International Monetary Fund.