The Federal Reserve's interest rate, commonly known as "Fed Rates," plays a crucial role in shaping the U.S. economy and influencing global financial markets. As one of the most powerful economic tools, the Fed Rates affect everything from borrowing costs to investment decisions. Understanding how these rates work is essential for anyone looking to make informed financial decisions.
Fed Rates are set by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), which evaluates economic conditions and adjusts rates to achieve stable prices and maximum employment. This mechanism ensures that the economy remains balanced and resilient against external shocks. The decisions made by the FOMC have far-reaching consequences, impacting everything from mortgage rates to stock market performance.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Fed Rates, exploring their impact on the economy, how they are determined, and what they mean for individuals and businesses. Whether you're an investor, a homeowner, or simply someone interested in understanding the broader economic landscape, this guide will provide you with the insights you need to navigate the financial world.
Read also:Understanding Freeze Warning A Comprehensive Guide To Stay Safe During Cold Weather
Table of Contents
- What Are Fed Rates?
- How Are Fed Rates Determined?
- Impact of Fed Rates on the Economy
- Effects on Personal Finance
- Historical Perspective of Fed Rates
- Current Fed Rate Trends
- Future Predictions for Fed Rates
- International Impact of Fed Rates
- Frequently Asked Questions About Fed Rates
- Conclusion
What Are Fed Rates?
Fed Rates refer to the interest rate set by the Federal Reserve, the central bank of the United States. This rate is the benchmark for all other interest rates in the country and serves as a tool for controlling inflation and unemployment. The Fed Rates are officially known as the Federal Funds Rate, which is the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to other banks on an overnight basis.
Key Functions of Fed Rates
- Regulating the money supply in the economy
- Influencing inflation and employment levels
- Stabilizing financial markets during periods of economic uncertainty
By adjusting the Fed Rates, the Federal Reserve can either stimulate economic growth or slow it down to prevent overheating. This delicate balancing act is crucial for maintaining economic stability.
How Are Fed Rates Determined?
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meets eight times a year to evaluate economic conditions and decide on the appropriate level for Fed Rates. During these meetings, committee members analyze various economic indicators, such as inflation rates, unemployment figures, and GDP growth, to determine whether to raise, lower, or maintain the current rates.
Factors Influencing Fed Rates
- Inflation: Higher inflation may lead to rate increases to curb spending.
- Unemployment: Lower unemployment rates may prompt rate hikes to prevent overheating.
- Economic Growth: Strong GDP growth could necessitate higher rates to control inflation.
The FOMC's decisions are guided by its dual mandate of promoting maximum employment and stable prices, ensuring that the economy remains on a sustainable growth path.
Impact of Fed Rates on the Economy
Fed Rates have a profound impact on the overall economy, influencing everything from business investments to consumer spending. When rates are low, borrowing becomes cheaper, encouraging businesses to expand and consumers to spend more. Conversely, higher rates can slow down economic activity by making borrowing more expensive.
Key Economic Effects
- Business Investment: Low rates encourage companies to invest in new projects and expand operations.
- Consumer Spending: Affordable borrowing costs boost consumer confidence and spending.
- Stock Market Performance: Lower rates often lead to increased stock prices as companies benefit from cheaper financing.
Understanding the relationship between Fed Rates and economic performance is vital for both policymakers and individuals seeking to make informed financial decisions.
Read also:Xavier Vs Texas A Comprehensive Analysis And Comparison
Effects on Personal Finance
Fed Rates also have a significant impact on personal finances, affecting everything from mortgage payments to savings account returns. When rates rise, borrowing costs increase, making it more expensive to take out loans or use credit cards. On the other hand, savers may benefit from higher returns on their deposits.
Impact on Different Financial Products
- Mortgages: Higher Fed Rates lead to increased mortgage rates, impacting homebuyers and homeowners.
- Credit Cards: Rising rates result in higher interest charges on credit card balances.
- Savings Accounts: Savers may see better returns on their deposits as rates increase.
Staying informed about Fed Rates can help individuals plan their finances more effectively, ensuring they are prepared for any changes in the economic environment.
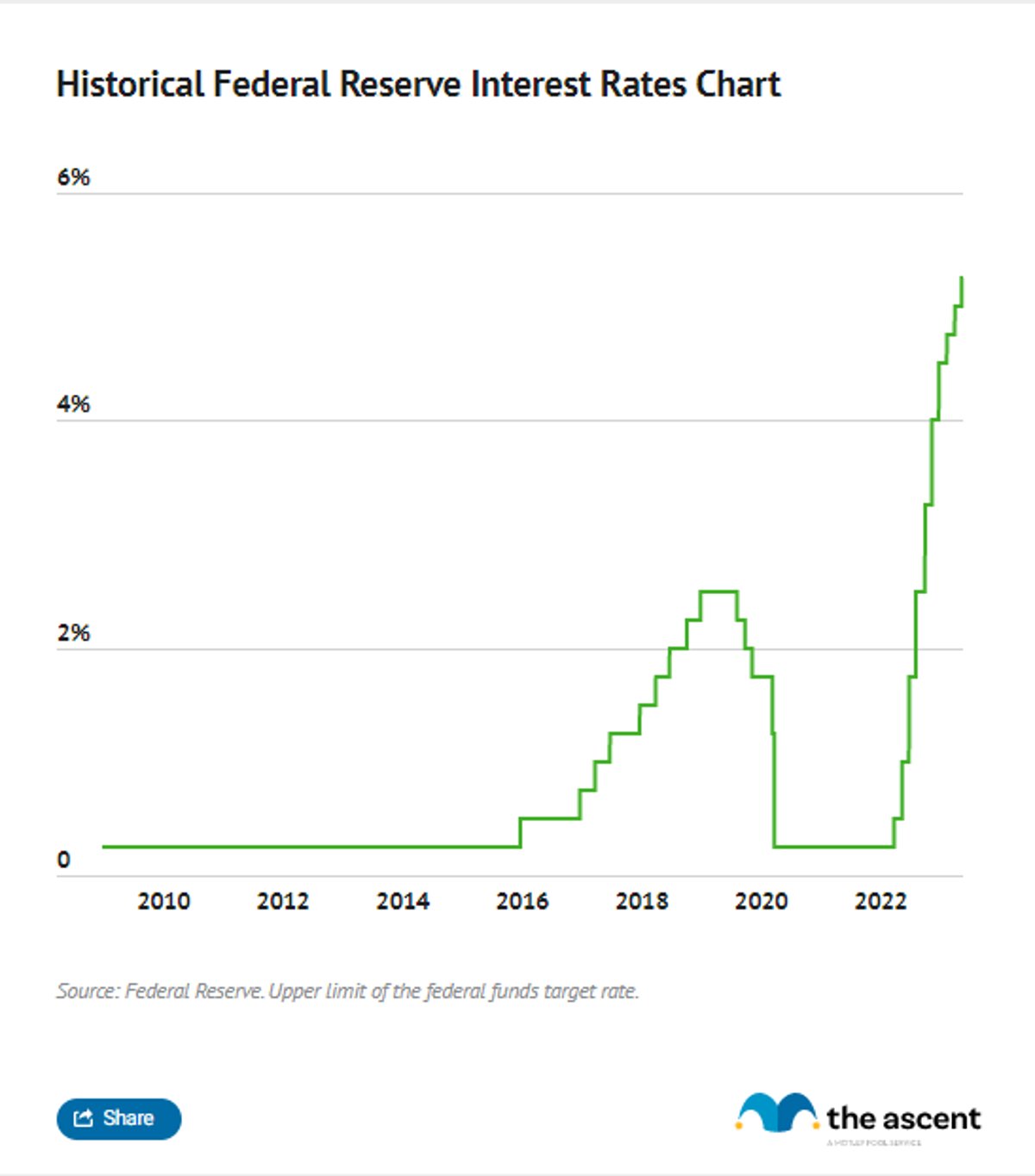
Historical Perspective of Fed Rates
Over the years, Fed Rates have fluctuated significantly, reflecting the changing economic conditions of the times. From the high rates of the 1980s, designed to combat rampant inflation, to the near-zero rates during the 2008 financial crisis, the Fed has used its monetary policy tools to address various economic challenges.
Notable Historical Trends
- 1980s: Double-digit rates to control inflation.
- 2008: Near-zero rates to stimulate economic recovery.
- 2020s: Gradual rate increases to manage post-pandemic growth.
Examining the historical context of Fed Rates provides valuable insights into how the Federal Reserve has navigated complex economic situations and adapted its policies to meet evolving needs.
Current Fed Rate Trends
As of the latest FOMC meetings, Fed Rates have been gradually increasing to address inflationary pressures. The Federal Reserve has signaled its intent to continue raising rates in the coming months, aiming to bring inflation under control without stifling economic growth.
Recent Developments
- 2023 Rate Increases: Several rate hikes have been implemented to combat rising inflation.
- Market Reactions: Stock markets have shown mixed reactions, with some sectors benefiting from higher rates.
- Consumer Impact: Borrowing costs have increased, affecting both businesses and individuals.
Keeping abreast of current trends in Fed Rates is essential for understanding the direction of the economy and making informed financial decisions.
Future Predictions for Fed Rates
Looking ahead, economists and analysts predict that Fed Rates will continue to rise in the short term, as the Federal Reserve works to bring inflation back to its target level. However, the long-term trajectory will depend on various factors, including global economic conditions and domestic policy decisions.
Potential Scenarios
- Stable Growth: Gradual rate increases to support steady economic expansion.
- Recession Risk: Possible rate cuts if economic conditions worsen.
- Inflation Surge: Further rate hikes if inflation remains persistently high.
Staying informed about potential future scenarios can help individuals and businesses prepare for any changes in the economic landscape.
International Impact of Fed Rates
Fed Rates also have a significant impact on the global economy, influencing currency values, trade balances, and investment flows. As the world's largest economy, the United States' monetary policy decisions reverberate across international markets, affecting countries and regions worldwide.
Global Consequences
- Currency Movements: Higher Fed Rates can strengthen the U.S. dollar, affecting trade balances.
- Emerging Markets: Rising rates can lead to capital outflows from developing economies.
- Investment Flows: Global investors may shift their focus to U.S. assets as rates increase.
Understanding the international implications of Fed Rates is crucial for businesses operating in a globalized economy and investors seeking opportunities in international markets.
Frequently Asked Questions About Fed Rates
Here are some common questions and answers about Fed Rates:
What Causes Fed Rates to Change?
Fed Rates change based on economic conditions, including inflation, unemployment, and GDP growth. The FOMC evaluates these factors during its regular meetings to determine the appropriate rate adjustments.
How Do Fed Rates Affect Mortgage Rates?
Mortgage rates are closely tied to Fed Rates. When the Fed raises rates, mortgage rates typically increase, making it more expensive for homebuyers to secure loans.
Why Are Fed Rates Important for Investors?
Fed Rates influence stock market performance, bond yields, and overall investment returns. Understanding rate changes can help investors make informed decisions about asset allocation and risk management.
Conclusion
Fed Rates play a critical role in shaping the U.S. economy and influencing global financial markets. By understanding how these rates are determined and their impact on various aspects of the economy, individuals and businesses can make more informed financial decisions. Whether you're managing personal finances or overseeing corporate investments, staying informed about Fed Rates is essential for navigating the complexities of the modern economic landscape.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and questions about Fed Rates in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into economic trends and financial strategies.