The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) plays a pivotal role in shaping the economic landscape of the United States. As one of the most influential bodies in the Federal Reserve System, the FOMC is tasked with making critical decisions regarding monetary policy, influencing interest rates, and ensuring economic stability. Understanding the FOMC's functions and decisions is essential for anyone interested in economics, finance, or investment.
The FOMC is a key player in the financial world, and its actions have far-reaching implications for both domestic and global economies. By setting monetary policy, the committee directly impacts inflation, employment rates, and overall economic growth. Its decisions can influence stock markets, bond yields, and currency values, making it a focal point for investors and policymakers alike.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the workings of the FOMC, its responsibilities, and how its decisions affect the economy. Whether you're a student, investor, or simply curious about how monetary policy impacts your daily life, this article will provide you with a thorough understanding of the FOMC's role and significance.
Read also:Duplicity Tyler Perry Exploring The Depths Of His Acting Versatility
Table of Contents
- What is the FOMC?
- FOMC Members and Structure
- Monetary Policy and the FOMC
- FOMC Meetings and Their Importance
- Understanding FOMC Statements
- The Impact of FOMC Decisions on the Economy
- How Investors Interpret FOMC Decisions
- A Historical Perspective on the FOMC
- Challenges Faced by the FOMC
- Conclusion and Next Steps
What is the FOMC?
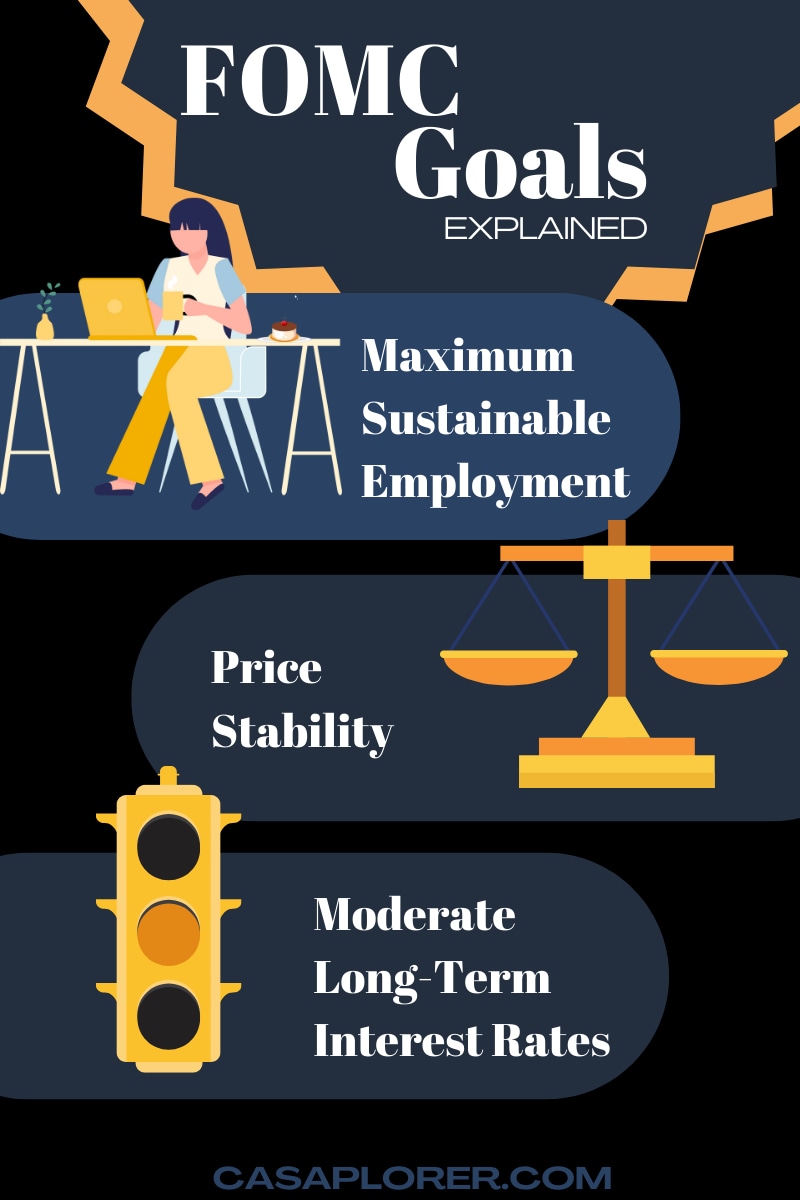
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is the monetary policymaking body of the Federal Reserve System. Established in 1913 under the Federal Reserve Act, the FOMC is responsible for implementing monetary policy to promote maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. It achieves this by conducting open market operations, setting target federal funds rates, and adjusting reserve requirements.
The FOMC operates under the broader umbrella of the Federal Reserve, which serves as the central banking system of the United States. By managing monetary policy, the FOMC aims to ensure economic stability and growth, while also addressing inflationary pressures and unemployment.
Purpose and Goals of the FOMC
The primary objectives of the FOMC are outlined in the Federal Reserve Act and include:
- Maximizing employment: Ensuring that the economy operates at full potential by reducing unemployment rates.
- Stabilizing prices: Controlling inflation to maintain purchasing power and economic stability.
- Promoting moderate long-term interest rates: Encouraging sustainable economic growth by balancing borrowing costs.
These goals are collectively referred to as the "dual mandate," emphasizing the committee's commitment to both employment and price stability.
FOMC Members and Structure
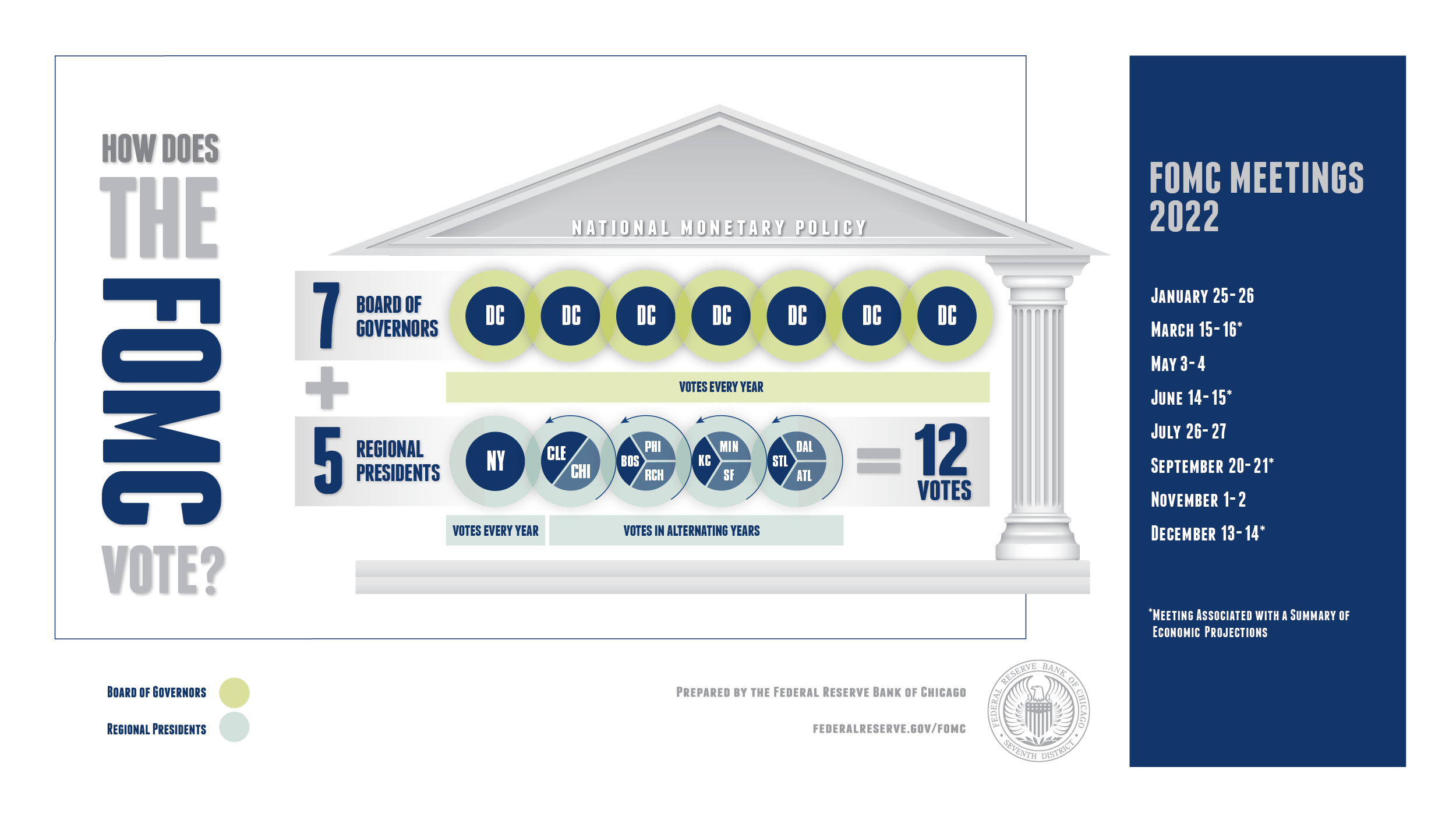
The FOMC consists of 12 members, including the seven members of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System and five of the 12 Federal Reserve Bank presidents. The President of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York serves as a permanent voting member, while the remaining four voting positions rotate annually among the other Reserve Bank presidents.
Structure and Roles
The structure of the FOMC ensures a balance between centralized authority and regional representation. Key roles include:
Read also:Julia Bachetti The Rise Of A Remarkable Figure In The Entertainment Industry
- Chair of the Federal Reserve: The Chair oversees the FOMC and plays a crucial role in shaping monetary policy decisions.
- Vice Chair: Assists the Chair and helps guide the committee's discussions and decisions.
- Regional Reserve Bank Presidents: Provide insights into local economic conditions, ensuring that regional perspectives are considered in policy decisions.
This diverse composition allows the FOMC to make informed decisions that reflect the broader economic landscape of the United States.
Monetary Policy and the FOMC
Monetary policy refers to the actions taken by the FOMC to influence the availability and cost of money and credit in the economy. The FOMC uses three primary tools to implement monetary policy:
- Open Market Operations: Buying and selling government securities to influence the federal funds rate.
- Federal Funds Rate: Setting a target range for the interest rate at which banks lend reserve balances to each other overnight.
- Reserve Requirements: Adjusting the amount of reserves banks must hold against deposits.
By adjusting these tools, the FOMC can influence economic activity, inflation, and employment levels.
Understanding the Tools of Monetary Policy
Each tool plays a unique role in shaping economic conditions:
- Open Market Operations: When the FOMC buys securities, it injects money into the economy, lowering interest rates. Conversely, selling securities reduces the money supply, raising interest rates.
- Federal Funds Rate: This rate directly affects borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, influencing spending and investment decisions.
- Reserve Requirements: Adjusting reserve requirements can control the amount of credit available in the economy.
These tools are carefully calibrated to achieve the FOMC's dual mandate of maximum employment and price stability.
FOMC Meetings and Their Importance
The FOMC holds eight regularly scheduled meetings each year, during which members review economic and financial conditions and determine appropriate monetary policy actions. These meetings are crucial for assessing the state of the economy and making informed decisions about interest rates and other policy measures.
Agenda and Decision-Making Process
During FOMC meetings, members discuss a wide range of economic indicators, including:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth.
- Inflation rates and consumer price index (CPI).
- Unemployment levels and labor market conditions.
- Global economic developments and financial market trends.
After thorough deliberation, the FOMC issues a statement summarizing its decisions and providing guidance on future policy actions.
Understanding FOMC Statements
FOMC statements are closely watched by economists, investors, and policymakers for insights into the committee's decision-making process and future policy intentions. These statements typically include:
- A summary of economic conditions and risks.
- A description of the committee's policy actions, such as changes to the federal funds rate.
- Forward guidance on the likely path of monetary policy.
Impact of FOMC Statements
FOMC statements can have significant effects on financial markets, influencing stock prices, bond yields, and currency values. Investors and analysts carefully parse these statements for clues about future economic conditions and policy changes.
The Impact of FOMC Decisions on the Economy
The decisions made by the FOMC have far-reaching consequences for the U.S. economy and beyond. By influencing interest rates and credit availability, the committee can stimulate or slow economic growth, manage inflation, and address unemployment.
Economic Effects of FOMC Policies
Key effects of FOMC policies include:
- Encouraging consumer spending and business investment through lower interest rates.
- Controlling inflation by raising interest rates when prices rise too quickly.
- Supporting job creation and reducing unemployment through accommodative monetary policies.
These effects underscore the critical role of the FOMC in maintaining economic stability and fostering growth.
How Investors Interpret FOMC Decisions
Investors closely monitor FOMC decisions and statements to gauge the future direction of interest rates and economic conditions. Changes in monetary policy can significantly impact asset prices, making it essential for investors to understand the committee's actions and intentions.
Investment Strategies Based on FOMC Decisions
Investors often adjust their strategies in response to FOMC decisions:
- Bond Markets: Rising interest rates typically lead to lower bond prices, while falling rates boost bond values.
- Stock Markets: Accommodative policies can boost equity prices, while tighter policies may lead to market corrections.
- Currency Markets: Higher interest rates tend to strengthen the U.S. dollar, while lower rates may weaken it.
By staying informed about FOMC policies, investors can better navigate the complexities of financial markets.
A Historical Perspective on the FOMC
The FOMC has played a crucial role in shaping economic policy throughout its history. From addressing the Great Depression to navigating the challenges of inflation, recessions, and financial crises, the committee has adapted its policies to meet evolving economic conditions.
Key Events in FOMC History
Notable moments in FOMC history include:
- The Volcker Era: Under Chairman Paul Volcker, the FOMC implemented tight monetary policies to combat high inflation in the 1980s.
- The Great Recession: During the 2008 financial crisis, the FOMC introduced unconventional measures, such as quantitative easing, to stabilize the economy.
- Post-Pandemic Recovery: In response to the COVID-19 pandemic, the FOMC implemented aggressive monetary policies to support economic recovery.
These events highlight the FOMC's adaptability and commitment to economic stability.
Challenges Faced by the FOMC
Despite its influence, the FOMC faces numerous challenges in implementing effective monetary policy. These challenges include:
- Global economic uncertainties and geopolitical risks.
- Changing demographics and labor market dynamics.
- Technological advancements and their impact on inflation and productivity.
Addressing Challenges Through Innovation
To address these challenges, the FOMC continues to refine its policies and approaches, leveraging data-driven analysis and innovative strategies to ensure economic stability and growth.
Conclusion and Next Steps
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) plays a vital role in shaping the economic landscape of the United States. By implementing monetary policy, the FOMC promotes maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. Understanding the FOMC's functions and decisions is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of economics and finance.
We encourage you to explore further resources and stay informed about FOMC developments. Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below, and consider exploring related articles on our site for a deeper understanding of economic topics. Together, we can build a more informed and resilient financial future.