Weather tornadoes are one of the most powerful and unpredictable natural phenomena on Earth, capable of causing catastrophic damage in seconds. They are nature's most violent storms, often leaving destruction in their wake and posing significant risks to life and property. Understanding the science behind these storms is crucial for preparedness and safety. This guide aims to provide detailed information about tornadoes, their causes, and how to stay safe during such events.
From the formation of a funnel cloud to the aftermath of a devastating tornado, this article explores every aspect of weather tornadoes. Whether you're a storm enthusiast, a concerned resident in a tornado-prone area, or simply curious about weather patterns, this guide offers valuable insights to help you better understand and prepare for these extreme weather events.
Our focus is not only on educating readers about the science of tornadoes but also on equipping them with practical knowledge to protect themselves and their loved ones. Let's delve into the world of tornadoes and uncover the mysteries behind these powerful forces of nature.
Read also:Australia Vs Indonesia Exploring The Cultural Economic And Geopolitical Ties
What Are Weather Tornadoes?
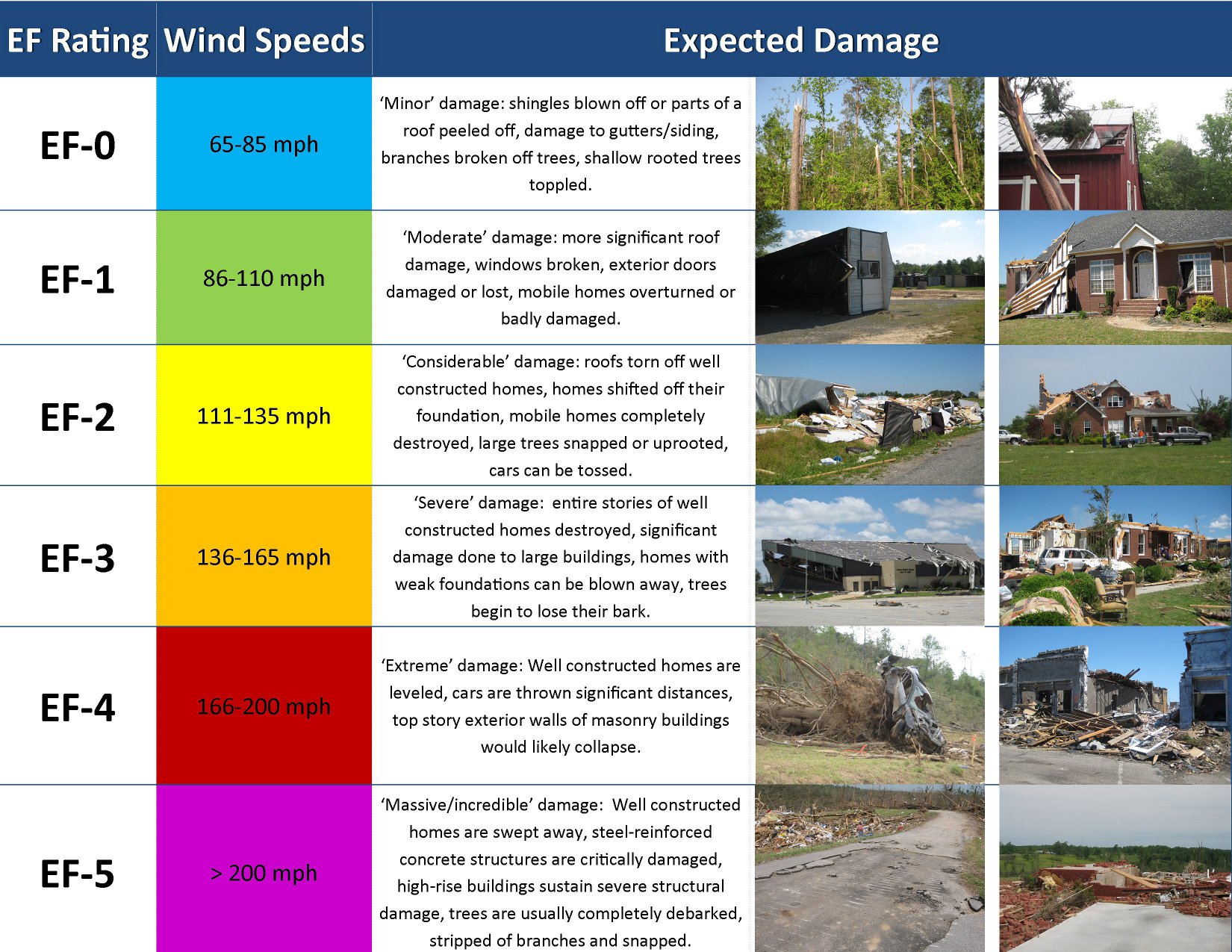
Weather tornadoes, commonly referred to simply as tornadoes, are violently rotating columns of air that extend from a thunderstorm to the ground. They are typically shaped like funnels, with diameters ranging from a few yards to more than a mile. Tornadoes are categorized by their intensity, measured using the Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale, which ranges from EF0 (weakest) to EF5 (strongest).
While tornadoes can occur anywhere in the world, they are most common in the United States, particularly in an area known as "Tornado Alley," which spans the central part of the country. This region experiences the highest frequency of tornadoes due to its unique geographical and atmospheric conditions.
Key Characteristics of Weather Tornadoes
- Speed: Tornado winds can reach speeds of up to 300 miles per hour, making them one of the fastest wind events on Earth.
- Duration: Most tornadoes last only a few minutes, but some can persist for over an hour, traveling long distances.
- Path: Tornadoes can follow erratic paths, sometimes changing direction suddenly, which makes them difficult to predict.
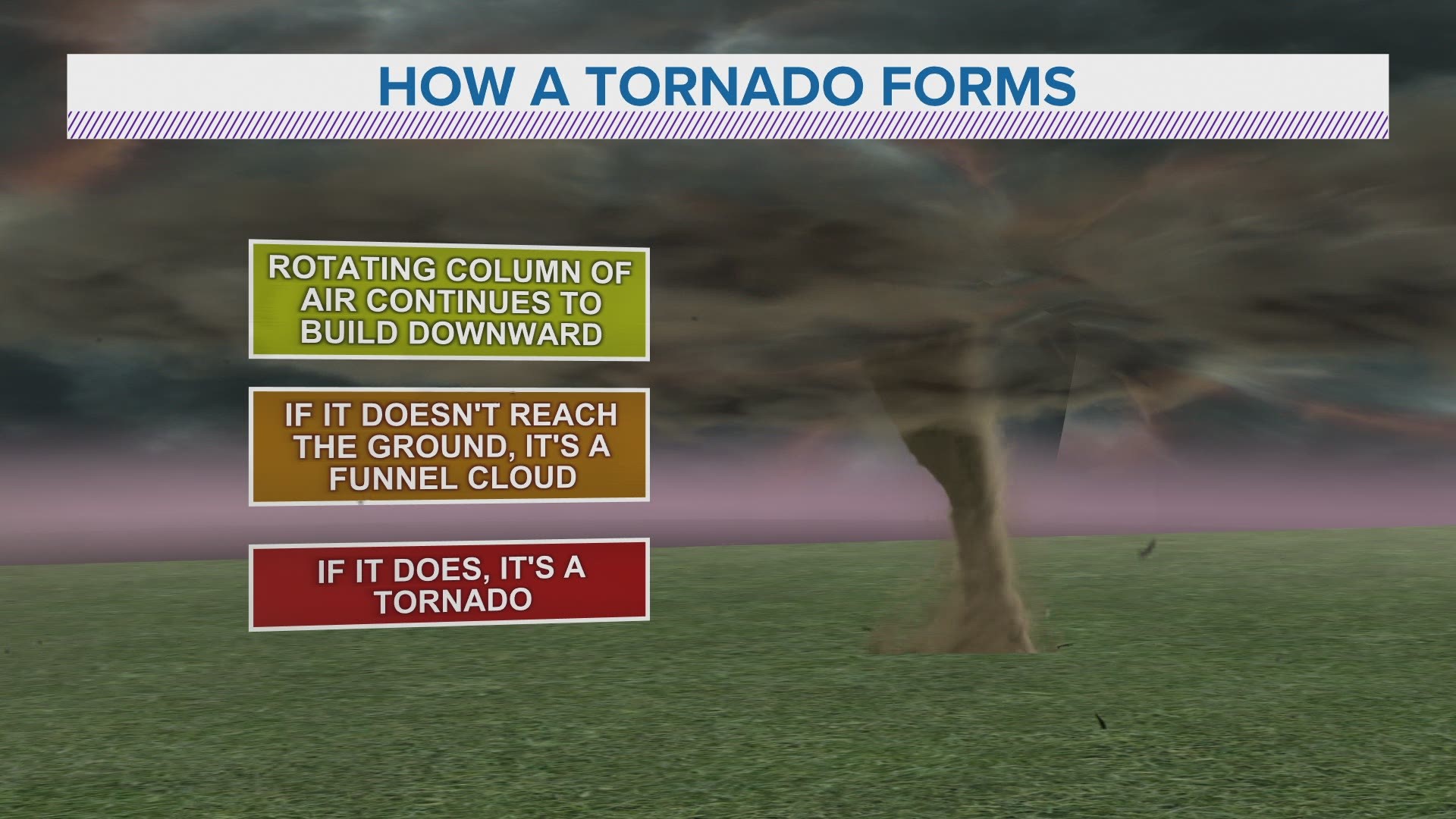
How Do Tornadoes Form?
The formation of tornadoes is a complex process involving specific atmospheric conditions. It begins with the development of a supercell thunderstorm, a type of storm characterized by a persistent rotating updraft. This rotation is crucial for tornado formation, as it creates a mesocyclone, which can eventually lead to the development of a tornado.
Factors Contributing to Tornado Formation
- Wind Shear: Changes in wind speed and direction with height create rotational motion in the atmosphere.
- Instability: Warm, moist air near the surface rises and meets cooler air aloft, creating instability that fuels thunderstorms.
- Lift: A front or other weather feature provides the necessary lift to initiate the thunderstorm process.
These factors work together to create the perfect conditions for tornado formation, often leading to severe weather outbreaks.
The Enhanced Fujita Scale
The Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale is used to rate the strength of tornadoes based on the damage they cause to buildings and vegetation. The scale ranges from EF0 to EF5, with EF5 being the most intense. Each category corresponds to a specific range of wind speeds and the level of destruction expected.
EF Scale Categories
- EF0: Winds 65-85 mph; minor damage to chimneys, branches broken off trees.
- EF1: Winds 86-110 mph; roofs peeled off houses, mobile homes overturned.
- EF2: Winds 111-135 mph; substantial damage to houses, large trees snapped.
- EF3: Winds 136-165 mph; severe damage to houses, trains overturned.
- EF4: Winds 166-200 mph; entire houses leveled, cars thrown.
- EF5: Winds over 200 mph; houses swept away, cars lifted and flown significant distances.
Tornado Alley: The Epicenter of Tornado Activity
Tornado Alley is a region in the central United States where tornadoes occur most frequently. This area is prone to tornadoes due to the convergence of warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and cool, dry air from the Rocky Mountains. The clash of these air masses creates the unstable atmospheric conditions necessary for tornado formation.
Read also:Sandro Mamukelashvili The Rising Star In European Basketball
States in Tornado Alley
- Texas
- Oklahoma
- Kansas
- Nebraska
- South Dakota
- Iowa
While Tornado Alley is the most famous region for tornado activity, other parts of the country, such as Dixie Alley in the southeastern United States, also experience frequent tornadoes.
Historical Tornado Events
Throughout history, there have been numerous significant tornado events that have left a lasting impact on communities and the scientific understanding of these storms. Some of the most notable events include the Tri-State Tornado of 1925, the 1947 Woodward Tornado, and the 2011 Joplin Tornado.
Tri-State Tornado of 1925
The Tri-State Tornado of March 18, 1925, is the deadliest tornado in U.S. history, causing 695 fatalities as it traveled through Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana. The tornado maintained an EF5 intensity for much of its path, traveling approximately 219 miles in just over three hours.
Staying Safe During a Tornado
Preparing for a tornado involves understanding the warning signs, having a safety plan, and knowing where to take shelter. The following tips can help ensure your safety during a tornado event.
Tornado Safety Tips
- Stay Informed: Monitor weather forecasts and alerts using reliable sources such as the National Weather Service.
- Identify Safe Shelter: Designate a safe room in your home, preferably a basement or an interior room on the lowest level.
- Prepare an Emergency Kit: Include essentials such as water, food, medications, flashlights, and a battery-powered radio.
Aftermath and Recovery
In the aftermath of a tornado, it is essential to assess the damage, ensure safety, and begin the recovery process. This involves checking for injuries, securing your property, and reaching out to emergency services if necessary.
Steps for Recovery
- Inspect Damage: Carefully evaluate the structural integrity of your home and report any issues to authorities.
- Seek Assistance: Contact insurance companies and disaster relief organizations for support in rebuilding.
- Stay Informed: Keep updated on recovery efforts and any additional safety warnings.
Scientific Research and Technological Advances
Advances in meteorology and technology have significantly improved our ability to predict and respond to tornadoes. Doppler radar, computer models, and satellite imagery are just a few of the tools used by scientists to study these storms and issue timely warnings.
Future Developments
Ongoing research aims to enhance our understanding of tornado dynamics and improve forecasting accuracy. Innovations such as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) and advanced sensors are being explored to gather more data on tornado formation and behavior.
Conclusion
Weather tornadoes are powerful and unpredictable forces of nature that require our respect and understanding. By learning about their formation, staying informed about potential threats, and preparing for emergencies, we can better protect ourselves and our communities. Remember to stay vigilant, follow safety guidelines, and share this knowledge with others.
We invite you to leave your thoughts and questions in the comments section below. For more information on weather phenomena and safety tips, explore our other articles. Together, we can build a safer and more informed future.
Table of Contents
- What Are Weather Tornadoes?
- How Do Tornadoes Form?
- The Enhanced Fujita Scale
- Tornado Alley: The Epicenter of Tornado Activity
- Historical Tornado Events
- Staying Safe During a Tornado
- Aftermath and Recovery
- Scientific Research and Technological Advances
- Conclusion