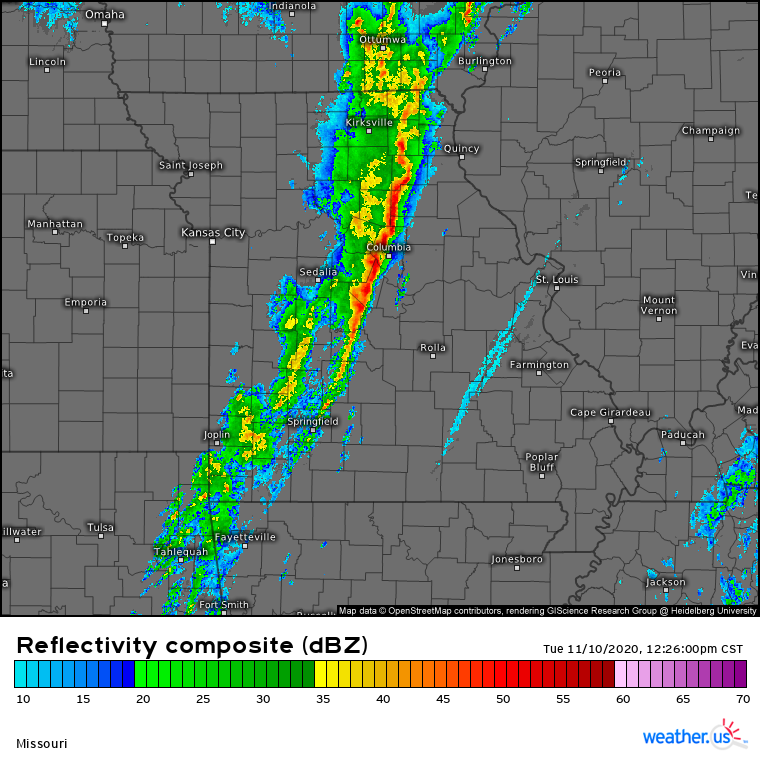
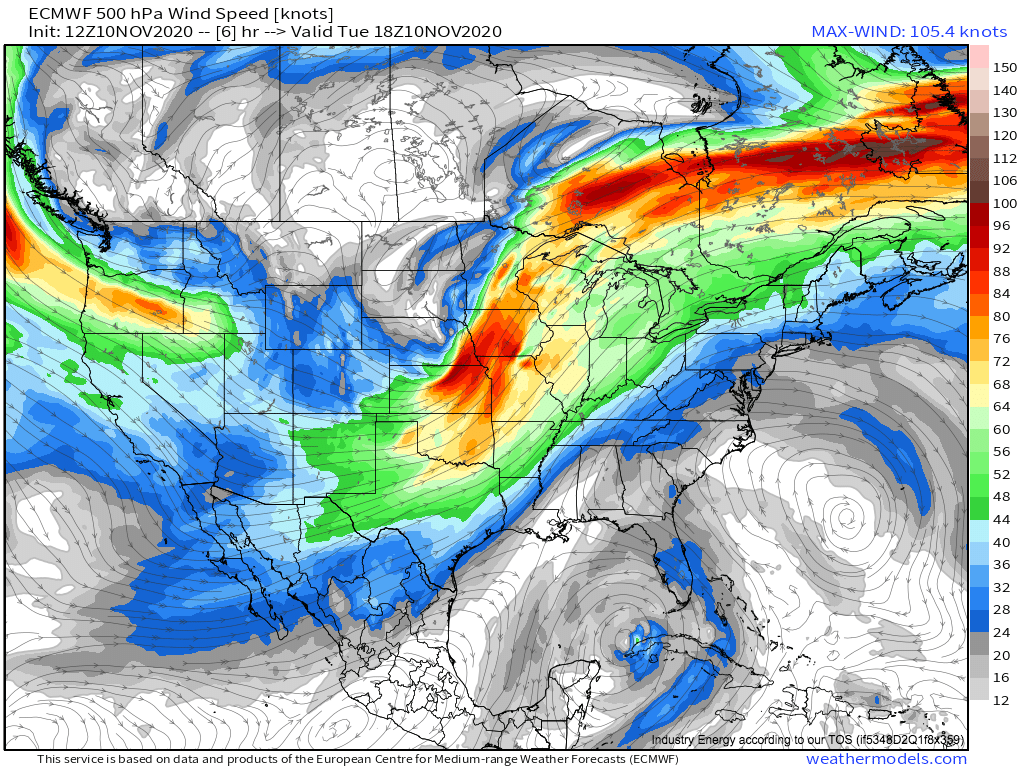
Severe thunderstorms in the Midwest pose a significant threat, with the potential to produce devastating tornadoes. These storms have long been a concern for residents in this region, as they can cause widespread damage and disrupt daily life. Understanding the dynamics of these storms is crucial for preparedness and safety.
The Midwest is no stranger to severe weather, and thunderstorms are a common occurrence during certain seasons. However, when these storms escalate, they can lead to tornadoes, which are among the most destructive natural phenomena. The unpredictability of tornadoes makes them particularly dangerous, emphasizing the importance of staying informed and prepared.
This article delves into the details of the Midwest severe thunderstorm threat, examining the factors that contribute to tornado formation, historical data, and strategies for staying safe. Whether you're a resident of the Midwest or simply interested in understanding severe weather patterns, this article provides comprehensive insights into the topic.
Read also:Hazing Runs Deep In Greek Life Southern Students Death Is A Painful Reminder Its Hard To Stop
Table of Contents
- Understanding Severe Thunderstorms
- How Tornadoes Form in Severe Thunderstorms
- Midwest Weather Patterns
- Historical Data of Tornadoes in the Midwest
- Risk Factors for Severe Thunderstorms
- Preparedness and Safety Measures
- Role of Technology in Forecasting
- Economic Impact of Severe Storms
- Community Efforts in Disaster Management
- Conclusion
Understanding Severe Thunderstorms
Severe thunderstorms are a common occurrence in many parts of the world, but the Midwest is particularly vulnerable due to its unique geographical positioning. These storms are characterized by strong winds, heavy rain, hail, and lightning, and in some cases, they can spawn tornadoes. The severity of these storms is influenced by several factors, including atmospheric instability and wind shear.
Key Characteristics:
- Strong winds exceeding 58 mph
- Hailstones larger than 1 inch in diameter
- Lightning strikes that pose a fire hazard
- Potential for tornado development
Understanding the mechanics of severe thunderstorms is essential for predicting their behavior and mitigating their impact. Meteorologists use advanced tools and models to track these storms, providing timely warnings to the public.
What Makes Thunderstorms Severe?
For a thunderstorm to be classified as severe, it must meet specific criteria set by meteorological organizations. These criteria include wind speed, hail size, and the presence of tornadoes. Severe thunderstorms often develop in environments with significant vertical wind shear and high levels of atmospheric instability, creating the perfect conditions for tornado formation.
How Tornadoes Form in Severe Thunderstorms
Tornadoes are one of the most dramatic and destructive outcomes of severe thunderstorms. They form when warm, moist air from the Gulf of Mexico collides with cool, dry air from the north, creating an unstable atmosphere. This instability, combined with wind shear, can lead to the formation of a rotating updraft known as a mesocyclone, which is the precursor to a tornado.
Steps in Tornado Formation:
Read also:Good American Family True Story A Journey Of Love Unity And Resilience
- Warm air rises and meets cooler air, creating instability
- Wind shear causes horizontal rotation in the air
- Rising air tilts the horizontal rotation into a vertical vortex
- The vortex tightens and intensifies, forming a funnel cloud
- The funnel cloud touches the ground, becoming a tornado
While tornadoes can occur anywhere, they are most common in the Midwest due to the region's unique geography and weather patterns.
EF Scale for Measuring Tornado Intensity
The Enhanced Fujita (EF) Scale is used to measure the intensity of tornadoes based on the damage they cause. This scale ranges from EF0 (minor damage) to EF5 (catastrophic damage). Understanding the EF scale is important for assessing the potential impact of a tornado and planning for safety.
Midwest Weather Patterns
The Midwest's weather patterns are influenced by its location at the intersection of several major weather systems. This region experiences a wide range of weather conditions throughout the year, from freezing winters to hot, humid summers. The convergence of warm and cold air masses frequently results in severe thunderstorms, making the Midwest a hotspot for tornado activity.
Key Weather Patterns:
- Spring and early summer are peak tornado seasons
- Thunderstorms often develop along cold fronts
- Moisture from the Gulf of Mexico fuels storm systems
Residents of the Midwest have learned to live with these weather patterns, developing strategies for coping with severe storms and minimizing their impact.
Geographical Factors Affecting Weather
The flat terrain of the Midwest allows storms to develop and travel unimpeded, increasing the likelihood of severe weather. Additionally, the region's proximity to the Gulf of Mexico provides a steady source of moisture, which contributes to the formation of powerful thunderstorms. Understanding these geographical factors is crucial for predicting and preparing for severe weather events.
Historical Data of Tornadoes in the Midwest
Historical data shows that the Midwest has experienced some of the most devastating tornadoes in recorded history. These events have left a lasting impact on the region, shaping its culture and infrastructure. By analyzing past tornado outbreaks, meteorologists can improve their forecasting models and better prepare for future events.
Notable Tornado Events:
- Tri-State Tornado of 1925 (EF5)
- 1999 Oklahoma Tornado Outbreak
- 2011 Joplin Tornado (EF5)
These events highlight the destructive power of tornadoes and underscore the importance of preparedness and resilience in the face of severe weather.
Trends in Tornado Frequency
Recent studies suggest that tornado frequency in the Midwest may be changing due to climate change. While the overall number of tornadoes has remained relatively stable, there has been an increase in the number of tornado outbreaks, where multiple tornadoes occur in a short period. Understanding these trends is essential for developing effective disaster management strategies.
Risk Factors for Severe Thunderstorms
Several risk factors contribute to the development of severe thunderstorms in the Midwest. These include atmospheric instability, wind shear, and moisture levels. Identifying and monitoring these factors is crucial for predicting severe weather events and issuing timely warnings.
Key Risk Factors:
- High levels of atmospheric instability
- Strong wind shear
- Abundant moisture supply
Meteorologists use advanced technology and data analysis to track these risk factors, providing valuable insights into the likelihood of severe thunderstorms and tornadoes.
Monitoring Severe Weather
Modern weather monitoring systems, such as Doppler radar and satellite imagery, play a critical role in detecting severe thunderstorms and tornadoes. These tools allow meteorologists to track storm systems in real-time, providing early warnings to the public and enabling timely evacuations when necessary.
Preparedness and Safety Measures
Preparedness is key to surviving severe thunderstorms and tornadoes in the Midwest. Residents should take steps to ensure their safety by staying informed, creating emergency plans, and assembling disaster supply kits. Education and community involvement are also important components of disaster preparedness.
Safety Tips:
- Stay informed through weather alerts and updates
- Create a family emergency plan
- Assemble a disaster supply kit
- Identify safe shelter locations
By taking these precautions, individuals and communities can reduce the risk of injury and loss during severe weather events.
Community Preparedness Programs
Many communities in the Midwest have established preparedness programs to educate residents about severe weather risks and provide resources for disaster planning. These programs often include workshops, drills, and information sessions, helping to build resilience at the local level.
Role of Technology in Forecasting
Advances in technology have revolutionized the field of weather forecasting, enabling meteorologists to predict severe thunderstorms and tornadoes with greater accuracy. Tools such as Doppler radar, satellite imagery, and computer models provide valuable data for tracking storm systems and issuing warnings.
Key Technologies:
- Doppler radar for tracking storm movement
- Satellite imagery for monitoring large-scale weather patterns
- Computer models for predicting storm development
These technologies have significantly improved the ability to forecast severe weather, saving lives and reducing property damage.
Challenges in Forecasting
Despite advances in technology, forecasting severe thunderstorms and tornadoes remains challenging due to the complex and dynamic nature of weather systems. Meteorologists must continuously refine their models and techniques to improve accuracy and reliability.
Economic Impact of Severe Storms
Severe thunderstorms and tornadoes have a significant economic impact on the Midwest, causing billions of dollars in damage each year. This impact is felt across various sectors, including agriculture, infrastructure, and insurance. Understanding the economic consequences of severe weather is essential for developing effective mitigation strategies.
Economic Costs:
- Damage to homes and businesses
- Loss of crops and livestock
- Increased insurance premiums
Governments and organizations are working to address these costs through disaster relief programs and infrastructure improvements, aiming to reduce the long-term economic burden of severe weather events.
Insurance and Recovery
Insurance plays a critical role in helping individuals and businesses recover from the financial impact of severe storms. Policies designed to cover tornado and hail damage provide essential support in the aftermath of a disaster, enabling faster recovery and rebuilding efforts.
Community Efforts in Disaster Management
Community involvement is vital for effective disaster management in the Midwest. By working together, residents, local governments, and organizations can enhance preparedness, response, and recovery efforts. Initiatives such as volunteer programs, public education campaigns, and emergency response drills help build resilience at the community level.
Community Initiatives:
- Volunteer disaster response teams
- Public education and awareness campaigns
- Emergency response drills and exercises
These efforts foster a sense of unity and cooperation, strengthening the community's ability to withstand and recover from severe weather events.
Conclusion
The Midwest severe thunderstorm threat, with its potential to produce tornadoes, is a significant concern for residents and stakeholders in the region. By understanding the factors that contribute to these storms, historical data, and risk factors, individuals and communities can better prepare for and respond to severe weather events. Advances in technology and community efforts have improved forecasting and disaster management, reducing the impact of these storms.
We encourage readers to stay informed, create emergency plans, and participate in community preparedness programs. Your actions can make a difference in ensuring the safety and resilience of the Midwest in the face of severe weather. Share this article with others and explore related content on our site to deepen your understanding of this critical topic.