Wisconsin hardiness zone is a crucial concept for gardeners, landscapers, and anyone interested in planting and cultivating plants in the state. Understanding the hardiness zones in Wisconsin can significantly impact the success of your gardening endeavors. Whether you're planting flowers, vegetables, or trees, knowing which plants thrive in your specific zone is essential for a flourishing garden.
Wisconsin's climate is diverse, ranging from cold winters to warm summers. This variability affects the types of plants that can survive and thrive in different parts of the state. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a detailed guide to help gardeners navigate these challenges. By familiarizing yourself with the Wisconsin hardiness zone, you can make informed decisions about the best plants for your garden.
This article will delve into the intricacies of the Wisconsin hardiness zone, offering valuable insights and practical tips for gardeners. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced gardener, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to create a thriving garden tailored to your region's unique conditions.
Read also:Tesla Crash Concerns Over Musks Power A Comprehensive Analysis
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Hardiness Zones
- Wisconsin Hardiness Zone Overview
- Understanding USDA Hardiness Zone Map
- Climate Characteristics of Wisconsin
- Plants Suited for Wisconsin Hardiness Zone
- Gardening Tips for Wisconsin Zones
- Common Challenges in Wisconsin Gardening
- Seasonal Planting Guides
- Case Studies of Successful Wisconsin Gardens
- Resources for Wisconsin Gardeners
Introduction to Hardiness Zones
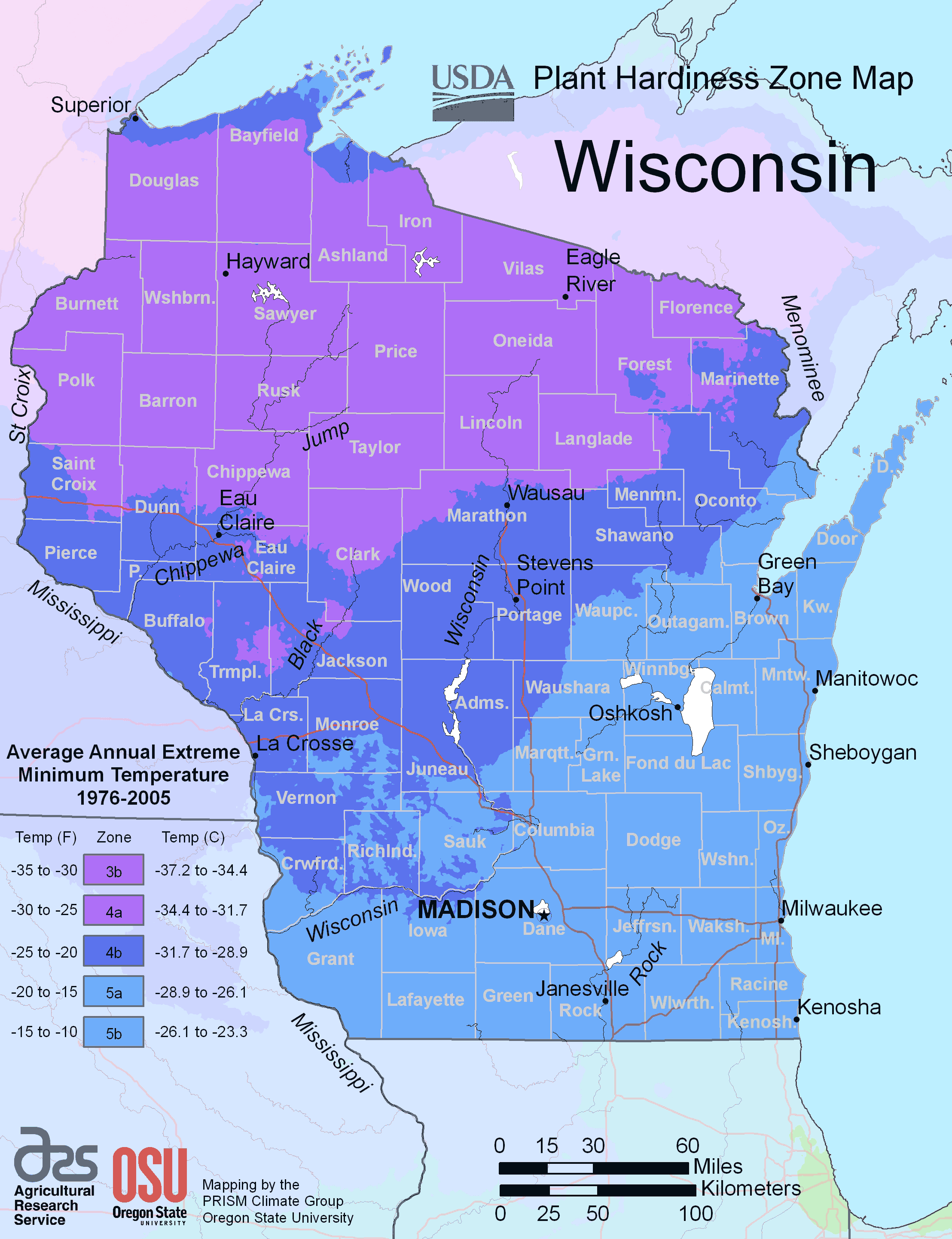
Hardiness zones are geographical areas defined by their climatic conditions, particularly the average annual minimum temperatures. These zones help gardeners and horticulturists determine which plants are most likely to thrive in a particular region. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides the United States into 13 zones, each representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit range of minimum temperatures.
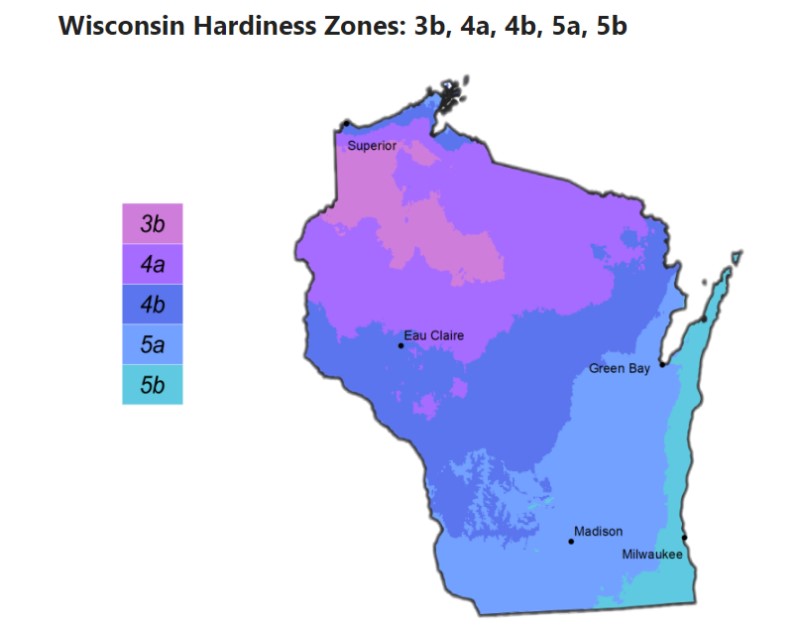
In Wisconsin, the hardiness zones range from 3a to 5b, depending on the specific location within the state. These variations reflect the diverse climate conditions across Wisconsin, from the colder northern regions to the relatively milder southern areas. Understanding these zones is vital for selecting plants that can withstand the local weather conditions.
Wisconsin Hardiness Zone Overview
The Wisconsin hardiness zone is an essential consideration for gardeners in the state. The USDA map provides a detailed breakdown of the zones, allowing gardeners to pinpoint their specific location's hardiness zone. Here’s a quick overview:
- Zone 3a: Average minimum temperature of -40 to -35°F
- Zone 3b: Average minimum temperature of -35 to -30°F
- Zone 4a: Average minimum temperature of -30 to -25°F
- Zone 4b: Average minimum temperature of -25 to -20°F
- Zone 5a: Average minimum temperature of -20 to -15°F
- Zone 5b: Average minimum temperature of -15 to -10°F
These zones provide a framework for selecting plants that can survive the coldest temperatures in each area.
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zone Map
How the Map Works
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable tool for gardeners. It uses data collected over decades to determine the average annual minimum temperatures for different regions. This map is updated periodically to reflect changes in climate patterns. By consulting the map, gardeners can identify their specific hardiness zone and choose plants accordingly.
Importance of the Map
The USDA Hardiness Zone Map is more than just a reference guide. It helps gardeners avoid costly mistakes by ensuring they select plants that are suited to their local climate. This knowledge is particularly important in regions like Wisconsin, where the climate can vary significantly from one area to another.
Read also:Camilla Row And Brennan Elliott A Deep Dive Into Their Journey Achievements And Impact
Climate Characteristics of Wisconsin
Winter Conditions
Wisconsin experiences harsh winters, with temperatures often dropping below freezing. Snowfall is common, and the ground may remain frozen for several months. These conditions make it challenging for certain plants to survive, highlighting the importance of selecting cold-hardy varieties.
Summer Conditions
Summers in Wisconsin are generally warm and humid, with temperatures ranging from 70°F to 90°F. This climate is ideal for many types of plants, including vegetables and flowers. However, gardeners must be mindful of potential droughts and ensure proper watering to maintain healthy plants.
Plants Suited for Wisconsin Hardiness Zone
Flowering Plants
Many beautiful flowering plants thrive in Wisconsin's hardiness zones. Some popular choices include:
- Daylilies
- Hostas
- Lilacs
- Purple Coneflowers
Vegetables
Gardeners in Wisconsin can grow a wide variety of vegetables, including:
- Carrots
- Peppers
- Tomatoes
- Zucchini
Gardening Tips for Wisconsin Zones
Preparing the Soil
Healthy soil is the foundation of a successful garden. In Wisconsin, gardeners should focus on improving soil quality by adding organic matter, such as compost or manure. This enhances soil fertility and structure, promoting strong plant growth.
Proper Watering Techniques
Watering is crucial, especially during dry spells. Gardeners should water deeply and less frequently to encourage deep root growth. Mulching can also help retain soil moisture and regulate temperature.
Common Challenges in Wisconsin Gardening
Frost Damage
Frost can damage or kill plants, particularly in early spring or late fall. Gardeners should monitor weather forecasts and take protective measures, such as covering plants or using frost blankets, when frost is expected.
Pests and Diseases
Pests and diseases can pose significant challenges for Wisconsin gardeners. Regularly inspecting plants for signs of infestation or disease is essential. Implementing integrated pest management (IPM) strategies can help control these issues effectively.
Seasonal Planting Guides
Spring Planting
Spring is an excellent time for planting in Wisconsin. Cool-season crops like lettuce, spinach, and peas can be planted as soon as the soil is workable. Hardy perennials and shrubs can also be planted during this time.
Summer Planting
Summer is ideal for planting warm-season crops such as tomatoes, peppers, and squash. Gardeners should ensure adequate watering and mulching to protect plants from the heat.
Case Studies of Successful Wisconsin Gardens
Garden A: Urban Backyard Garden
Located in Milwaukee, this garden features a mix of vegetables and flowers. The gardener uses raised beds to improve soil quality and employs drip irrigation to conserve water. This garden thrives despite the urban environment, producing an abundance of fresh produce.
Garden B: Rural Flower Garden
In the countryside of Wisconsin, this garden showcases a stunning array of flowers. The gardener selects plants based on their hardiness zone and uses natural pest control methods to maintain a healthy ecosystem. The result is a vibrant and sustainable garden.
Resources for Wisconsin Gardeners
Local Extension Services
Wisconsin's extension services offer valuable resources for gardeners, including workshops, publications, and expert advice. These services are invaluable for learning about the latest gardening techniques and plant varieties suited to the local climate.
Online Resources
Several online platforms provide information on Wisconsin hardiness zones and gardening tips. Websites such as the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and the University of Wisconsin-Madison Extension website are excellent resources for gardeners seeking reliable information.
Kesimpulan
Understanding the Wisconsin hardiness zone is essential for successful gardening in the state. By selecting plants suited to your specific zone and following best gardening practices, you can create a thriving garden that withstands Wisconsin's diverse climate. We encourage you to explore the resources available and share your gardening experiences with others. Your feedback and insights can help fellow gardeners grow and learn.
Feel free to leave a comment or question below. Share this article with other gardening enthusiasts and explore our other articles for more tips and tricks to enhance your gardening skills. Happy gardening!