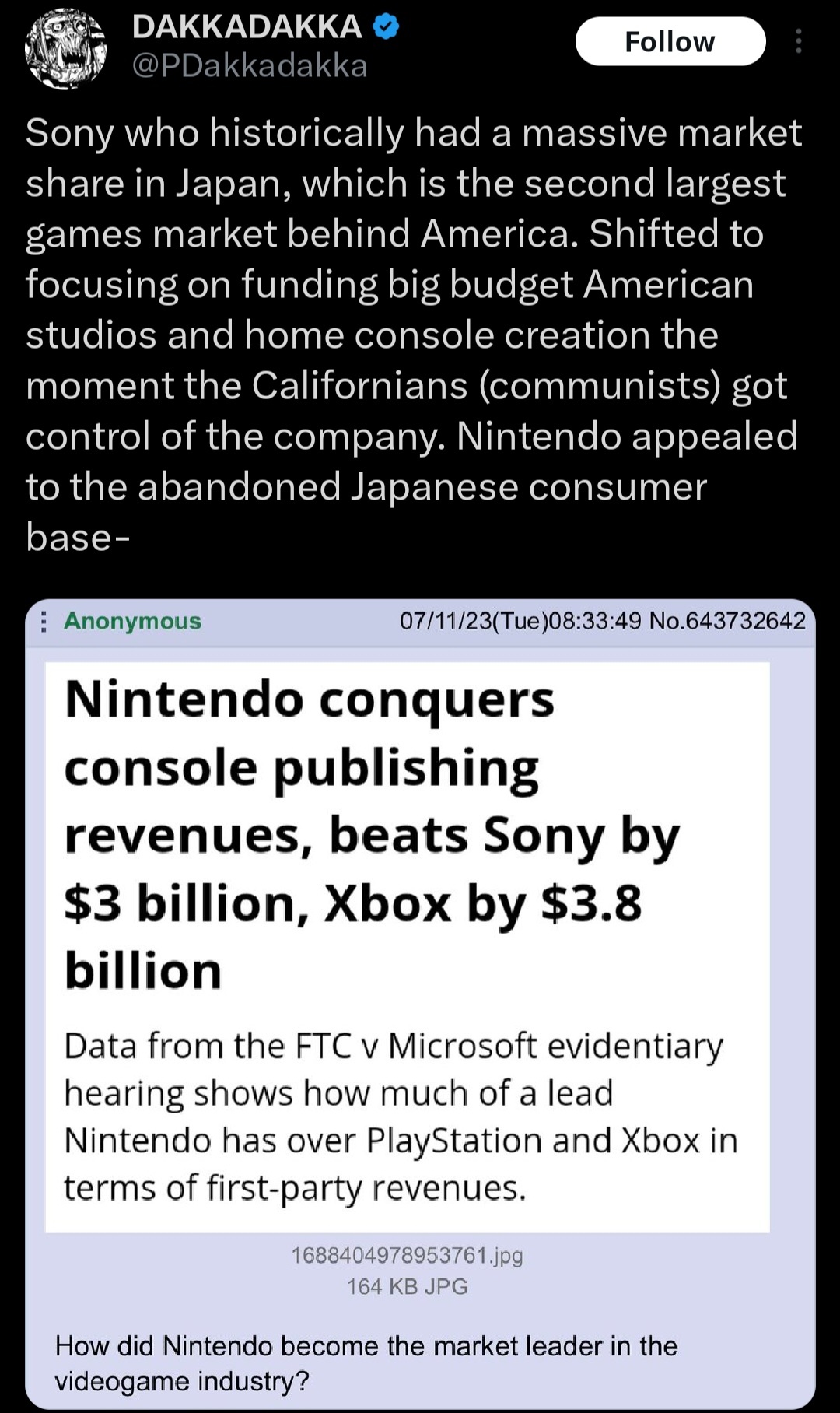
Trans animals have become an intriguing subject of study in recent years, shedding light on the fascinating world of gender diversity in nature. Many people are unaware that gender fluidity is not exclusive to humans but also occurs in various animal species. This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of trans animals, exploring their characteristics, behaviors, and significance in the ecosystem.
From intersex fish to gender-switching reptiles, the animal kingdom showcases an incredible array of biological diversity. Scientists have discovered that many species exhibit behaviors and physical traits that challenge traditional notions of gender and sexuality. This challenges us to rethink our understanding of nature and embrace the complexity of life.
This article will provide an in-depth look at trans animals, covering everything from scientific research to real-life examples. By the end of this guide, you will have a better understanding of how gender diversity exists in nature and why it matters for conservation efforts and scientific research.
Read also:Vanessa Hudgens Nude Photos Leaked A Comprehensive Analysis And Faqs
What Are Trans Animals?
Trans animals refer to species that exhibit gender transitions, intersex characteristics, or behaviors that defy traditional binary gender classifications. These animals may change their sex during their lifetime, possess both male and female reproductive organs, or display behaviors typically associated with the opposite gender. This phenomenon has been observed in various species, including fish, reptiles, amphibians, and even some mammals.
One of the most well-documented examples of trans animals is the clownfish, which can change its gender based on social hierarchies. In certain species of coral reef fish, dominant females can transform into males when the dominant male dies or leaves the group. This adaptation allows for more efficient reproduction and survival in changing environments.
Biological Mechanisms Behind Trans Animals
The biological mechanisms behind gender transitions in animals vary depending on the species. Hormonal changes, environmental factors, and social dynamics all play a role in determining an animal's gender expression. For example, certain fish species undergo hormonal shifts that trigger sex changes, while some reptiles rely on temperature-dependent sex determination during embryonic development.
Here are some key factors influencing trans animals:
- Hormonal regulation
- Environmental triggers
- Social hierarchies
- Genetic predispositions
Examples of Trans Animals in Nature
Clownfish: Gender Transition in Coral Reefs
Clownfish, made famous by the movie "Finding Nemo," are one of the most well-known examples of trans animals. These small fish live in symbiosis with sea anemones and form social groups with a strict hierarchy. In these groups, the largest and most dominant fish is typically female, while the smaller fish are male. If the dominant female dies, the largest male can transition into a female, maintaining the group's reproductive balance.
Hermaphroditic Snails: Dual-Gendered Mollusks
Many species of snails are simultaneous hermaphrodites, meaning they possess both male and female reproductive organs. This adaptation allows them to reproduce more efficiently, as any encounter with another snail can result in fertilization. Some species even engage in "penis fencing," a behavior where two snails duel to determine which will act as the male and which as the female during mating.
Read also:Princess Beatrice Of York A Night To Remember At Bornes Wonderland Gala
Scientific Research on Trans Animals
Scientific research on trans animals has significantly advanced our understanding of gender diversity in nature. Studies conducted by institutions such as the Smithsonian Institution, the University of California, and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) have provided valuable insights into the biological and environmental factors influencing gender transitions in animals.
For example, a study published in the journal Science found that certain species of fish can change their gender in response to environmental stressors such as pollution or overfishing. These findings highlight the importance of protecting natural habitats to preserve the biodiversity of trans animals.
Conservation Efforts for Trans Animals
Conservation efforts for trans animals focus on preserving their habitats and addressing the environmental factors that threaten their survival. Climate change, habitat destruction, and pollution are among the primary challenges facing these species. Organizations such as the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) and the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) are working to protect trans animals by implementing sustainable practices and promoting public awareness.
One successful conservation project involves the protection of coral reefs, which serve as critical habitats for many trans animal species. By reducing carbon emissions, limiting overfishing, and promoting marine protected areas, conservationists hope to ensure the survival of these unique creatures.
Trans Animals and Human Perception
The study of trans animals has important implications for human understanding of gender and sexuality. By observing the natural world, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and diversity of life. This knowledge challenges traditional gender norms and encourages a more inclusive perspective on human identity.
Some researchers argue that studying trans animals can help reduce stigma surrounding gender non-conformity in human societies. By recognizing the prevalence of gender diversity in nature, we can foster greater acceptance and understanding of diverse gender expressions.
Challenges Facing Trans Animals
Despite their fascinating adaptations, trans animals face numerous challenges in the modern world. Environmental pollution, habitat loss, and climate change all threaten their survival. Additionally, human activities such as overfishing and coral bleaching exacerbate these issues, making it increasingly difficult for trans animals to thrive.
One major concern is the impact of endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs) on aquatic ecosystems. These chemicals, often found in industrial waste and agricultural runoff, can interfere with hormonal systems in fish and other aquatic species, leading to abnormal gender development and reproductive issues.
Economic and Ecological Importance of Trans Animals
Trans animals play a vital role in maintaining healthy ecosystems. For example, gender-changing fish help regulate population dynamics in coral reefs, ensuring balanced reproduction and resource distribution. Similarly, hermaphroditic mollusks contribute to soil health and nutrient cycling in terrestrial environments.
From an economic perspective, trans animals also have significant value. Many species, such as oysters and clams, are important sources of food and income for coastal communities. Protecting these species not only preserves biodiversity but also supports livelihoods and food security.
Myths and Misconceptions About Trans Animals
Myth: Gender Changes in Animals Are Rare
Contrary to popular belief, gender changes in animals are quite common in certain species. While not all animals exhibit this behavior, it is a well-documented phenomenon in many fish, reptiles, and mollusks. Scientists estimate that over 2,000 species of animals are capable of changing their gender at some point in their lives.
Myth: Trans Animals Are a Recent Discovery
Trans animals have been studied for decades, with early observations dating back to the 19th century. However, advances in technology and increased public interest have led to a surge in research and awareness in recent years. This renewed focus has helped debunk many myths and misconceptions surrounding gender diversity in nature.
Future Directions in Trans Animal Research
As our understanding of trans animals continues to grow, researchers are exploring new avenues for study. Advances in genetic engineering and biotechnology offer exciting possibilities for understanding the mechanisms behind gender transitions in animals. Additionally, interdisciplinary approaches combining biology, ecology, and social sciences can provide a more holistic perspective on this complex topic.
Future research may also focus on the potential applications of trans animal studies in medicine and biotechnology. For example, understanding the hormonal pathways involved in gender transitions could lead to new treatments for human gender dysphoria and other conditions.
Conclusion
Trans animals represent an incredible example of nature's adaptability and diversity. From clownfish to hermaphroditic snails, these creatures challenge traditional notions of gender and offer valuable insights into the complexities of life. By studying trans animals, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the natural world and promote greater acceptance of diversity in all its forms.
We encourage readers to share this article with others and explore related topics on our website. Together, we can promote awareness and understanding of trans animals and their importance in maintaining healthy ecosystems. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them below!
Table of Contents
- What Are Trans Animals?
- Biological Mechanisms Behind Trans Animals
- Examples of Trans Animals in Nature
- Scientific Research on Trans Animals
- Conservation Efforts for Trans Animals
- Trans Animals and Human Perception
- Challenges Facing Trans Animals
- Economic and Ecological Importance of Trans Animals
- Myths and Misconceptions About Trans Animals
- Future Directions in Trans Animal Research
- Conclusion