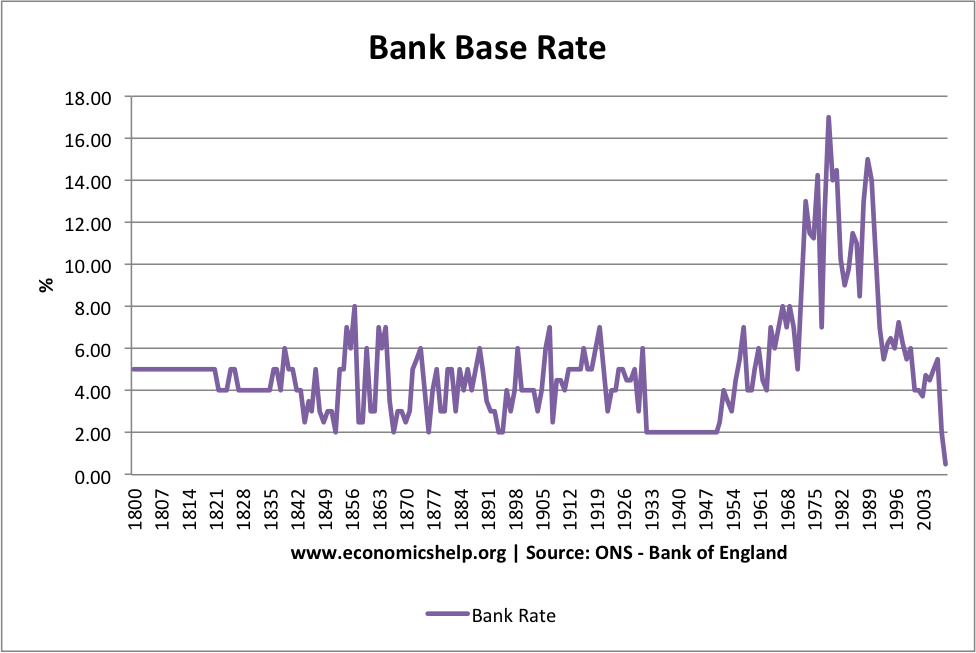
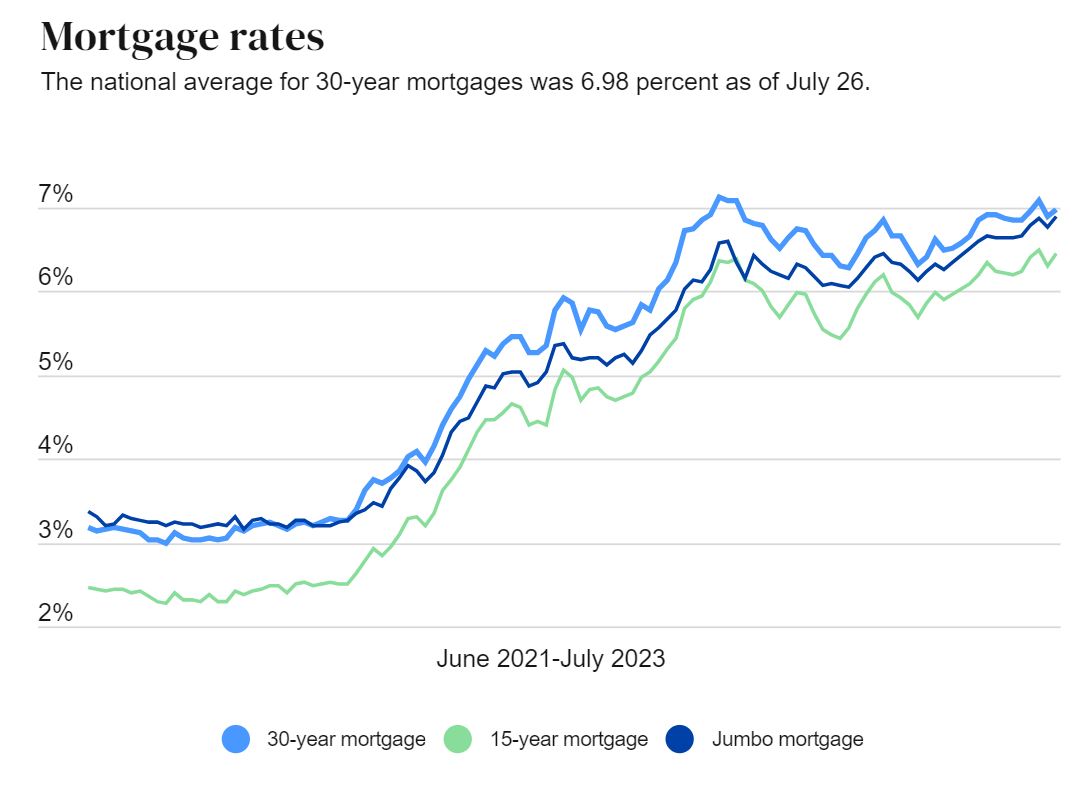
Interest rates play a pivotal role in shaping the global economy and influencing individual financial decisions. Whether you're saving, borrowing, or investing, understanding how interest rates work is crucial. They impact everything from mortgage payments to business loans and credit card debt. In this article, we will delve deep into the concept of interest rates, their types, and their effects on various aspects of personal and corporate finance.
As one of the most discussed topics in economics, interest rates are more than just numbers on a financial statement. They serve as a tool for central banks to regulate inflation, control economic growth, and manage monetary policy. By the end of this article, you will have a clear understanding of how interest rates influence your financial health and how you can leverage them to make informed decisions.
This guide is designed to provide actionable insights and expert advice to help you navigate the complexities of interest rates. From the basics to advanced strategies, we will cover everything you need to know to build a solid foundation in this critical area of finance.
Read also:Denver Nuggets Vs Lakers Match Player Stats A Comprehensive Analysis
Table of Contents
- What Are Interest Rates?
- Types of Interest Rates
- Factors Affecting Interest Rates
- The Role of Central Banks in Setting Interest Rates
- How Interest Rates Impact the Economy
- Interest Rates and Personal Finance
- Impact of Interest Rates on Businesses
- Historical Trends in Interest Rates
- Future Predictions for Interest Rates
- Conclusion
What Are Interest Rates?
Interest rates refer to the cost of borrowing money or the return earned on saved funds. Essentially, they represent the percentage charged or paid on a loan or deposit. This fundamental concept is central to the functioning of modern economies. For instance, when you take out a mortgage, the interest rate determines how much extra you will pay over the life of the loan.
Interest rates can be fixed or variable, depending on the agreement between the lender and borrower. Fixed rates remain constant throughout the loan term, while variable rates fluctuate based on market conditions. Understanding the distinction between these types is essential for making sound financial decisions.
How Are Interest Rates Calculated?
The calculation of interest rates involves several factors, including the principal amount, loan duration, and prevailing market conditions. Lenders assess risk and creditworthiness before determining the appropriate rate. For example, individuals with higher credit scores often qualify for lower interest rates due to their perceived lower risk of default.
Banks and financial institutions use complex formulas to calculate interest rates, ensuring they align with regulatory standards and market trends. This ensures fairness and transparency in the lending process.
Types of Interest Rates
Interest rates come in various forms, each serving a specific purpose. Below are the most common types:
- Nominal Interest Rate: The stated rate without considering inflation.
- Real Interest Rate: Adjusted for inflation, providing a more accurate reflection of purchasing power.
- Discount Rate: The rate charged by central banks to commercial banks for short-term loans.
- Prime Rate: The lowest rate offered to the most creditworthy customers by banks.
Understanding the differences between these rates is crucial for both consumers and businesses. Each type plays a unique role in shaping financial strategies and decision-making processes.
Read also:Alison Krauss A Voice That Transcends Time And Genre
Factors Affecting Interest Rates
Several key factors influence the movement of interest rates:
- Inflation: Higher inflation typically leads to higher interest rates as lenders seek to preserve the value of their returns.
- Economic Growth: Strong economic growth can lead to increased demand for loans, driving up interest rates.
- Central Bank Policies: Decisions made by central banks, such as adjusting benchmark rates, have a direct impact on interest rates.
- Global Events: Political instability, natural disasters, and other global events can create uncertainty, affecting interest rates.
By monitoring these factors, individuals and businesses can better anticipate changes in interest rates and adjust their financial plans accordingly.
The Role of Central Banks in Setting Interest Rates
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States and the European Central Bank, play a critical role in setting interest rates. They use monetary policy tools to influence economic conditions and maintain stability. For example, during periods of high inflation, central banks may raise interest rates to cool down the economy.
How Central Banks Influence the Economy
Central banks adjust interest rates to achieve specific economic goals, such as controlling inflation, boosting employment, and stabilizing currency values. By lowering rates, they encourage borrowing and spending, stimulating economic growth. Conversely, raising rates can help curb excessive spending and reduce inflationary pressures.
These actions have far-reaching effects on consumers, businesses, and global markets. Understanding the role of central banks is essential for anyone seeking to navigate the complexities of modern finance.
How Interest Rates Impact the Economy
Interest rates have a profound impact on the overall economy. They influence consumer spending, business investment, and government fiscal policies. For example, lower interest rates can lead to increased borrowing for home purchases and business expansion, boosting economic activity.
Conversely, higher interest rates can slow down economic growth by making borrowing more expensive. This can lead to reduced consumer spending and decreased business investment. Balancing these effects is a key challenge for policymakers and central banks.
Interest Rates and Personal Finance
Interest rates directly affect personal finance decisions, such as saving, borrowing, and investing. For instance, when interest rates are low, it may be an opportune time to take out a mortgage or refinance existing debt. Conversely, higher rates can make saving more attractive, as returns on savings accounts and certificates of deposit increase.
Tips for Managing Personal Finances During Interest Rate Changes
To effectively manage personal finances during periods of interest rate fluctuations, consider the following strategies:
- Monitor economic indicators to anticipate rate changes.
- Lock in favorable rates on long-term loans when rates are low.
- Explore investment opportunities that benefit from rising rates, such as bonds.
By staying informed and proactive, individuals can optimize their financial outcomes in response to changing interest rates.
Impact of Interest Rates on Businesses
Interest rates significantly impact businesses, affecting everything from borrowing costs to operational expenses. For example, higher interest rates can increase the cost of financing capital expenditures, such as purchasing new equipment or expanding facilities. This can strain cash flow and reduce profitability.
Conversely, lower interest rates can create opportunities for businesses to expand and invest in growth initiatives. Companies may also benefit from reduced borrowing costs, allowing them to allocate resources more efficiently.
Strategies for Businesses to Mitigate Interest Rate Risks
Businesses can implement several strategies to manage interest rate risks:
- Use fixed-rate loans to lock in favorable rates.
- Hedge against interest rate fluctuations using financial derivatives.
- Optimize cash flow management to maintain liquidity during periods of rate volatility.
These proactive measures can help businesses maintain financial stability and capitalize on opportunities presented by changing interest rates.
Historical Trends in Interest Rates
Examining historical trends in interest rates provides valuable insights into their behavior and potential future movements. For example, during the 1980s, interest rates in the United States reached historic highs as the Federal Reserve worked to combat rampant inflation. Conversely, the 2008 financial crisis led to record-low rates as central banks sought to stimulate economic recovery.
By studying these trends, analysts and policymakers can better predict future rate movements and develop strategies to address potential challenges.
Future Predictions for Interest Rates
Forecasting future interest rate movements involves analyzing a range of economic indicators and global trends. While predicting exact rates is challenging, experts generally agree that rates will remain relatively low in the near term due to ongoing economic recovery efforts. However, as inflationary pressures increase, central banks may gradually raise rates to maintain stability.
Staying informed about global economic developments and central bank policies is essential for anyone seeking to anticipate future interest rate changes and prepare accordingly.
Conclusion
In conclusion, interest rates are a critical component of modern finance, influencing everything from personal savings to global economic policies. Understanding their mechanics, types, and effects is essential for making informed financial decisions. By staying informed about economic trends and central bank policies, individuals and businesses can effectively navigate the complexities of interest rates and achieve their financial goals.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with interest rates in the comments section below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into personal finance, economics, and investment strategies. Together, let's build a stronger financial future!
![Buying a Home? Mortgage Rate Guide for Singapore [2023]](https://blog.roshi.sg/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Singapore-Home-Loan-Rates-2022.jpeg)